
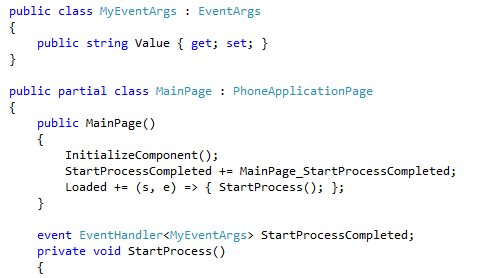
Option 1: The Event Pattern
One of the most common approaches is to create a void method that releases control and raises a Completed event when it is finished. Here’s how you implement that:
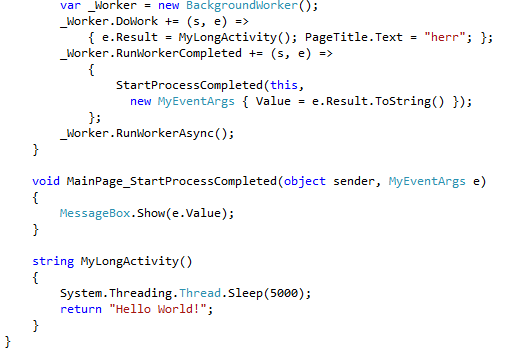
In the code above, look at MyLongActivity(). It’s not really a long activity, I just make it sleep for 5 seconds to simulate a long process. Now look at StartProcess(). StartProcess() is a wrapper that lets us call MyLongActivity() asynchronously. It starts MyLongActivity() on a background thread, then release control back to the caller.
See that BackgoundWorker? This is a great control. 1) It is available across every device and framework (making your implementations more consistent), 2) it is very simple to use, 3) it completes on the UI thread. That last part kills most developers.
Remember: we execute asynchronously on a non-UI thread so the UI continues moving. But, we can’t touch the UI thread from this background thread. If we try, we get this!:
Practice Safe Threading
First, the BackgroundWorker makes “returning to the UI thread” moot – it does it for you. But what if you want to anyway? Serious?! You nerds always want the details, don’t you? Okay. In Silverlight, we do this with the Dispatcher’s BeginInvoke() method:
Option 2: Callback Pattern
I am starting to like this pattern best. There are no events with callbacks. When the async operation is complete the callback is invoked. Since a callback is simply a method, your after-it’s-done logic is nicely packaged there (yes, like the completed event handler).However, using a callback means you don’t have to differentiate multiple completed events with a user state object. When a callback is invoked, the context is known and sure. The only drawback is that it is somewhat more complex, at first. Only at first:

In the code above, just look how much less code there is and how much more control you get over the context. See Callback()? That method is invoked at the end of the async operation. There are no events, no event arguments. Just simple methods.









0 comments:
Post a Comment